Financial institutions have been increasingly attacked by cybercriminals in recent years. In response, banks and other organizations have beefed up their cybersecurity measures. But what about ATMs? Are they safe from attack? This article takes a look at the current state of affairs for ATM security in India and what’s being done to prevent future attacks.
The current state of cybersecurity for ATMs in India
ATMs in India are currently facing a number of cybersecurity threats. These threats include skimming, malware attacks, and ATMjackings. In order to combat these threats, a number of measures have been put in place by the government and financial institutions.
Some of the measures that have been put in place include the installation of security cameras at ATMs, the use of chip-and-pin cards instead of magnetic stripe cards, and the deployment of security guards at high-risk ATMs. Additionally, the Reserve Bank of India has directed all banks to implement a “security operations centre” by March 2019. This centre will monitor ATM networks for suspicious activity and take appropriate action in the event of an attack.
Despite these measures, cybersecurity attacks on ATMs in India continue to occur. In May 2018, a group of hackers used skimming devices to steal over Rs 1 crore from ATMs across India. In September 2018, another group of hackers used malware to target ATMs in India and steal over Rs 2 crore.
These attacks highlight the need for improved cybersecurity measures for ATMs in India. The government and financial institutions must continue to work together to identify new threats and put in place effective countermeasures.
The different types of attacks that have occurred
Since the early 2010s, there have been a number of high-profile attacks on ATMs in India. In 2012, a group of attackers used skimming devices to steal over $1 million from ATMs in Mumbai. In 2013, another group used malware to infect ATMs and force them to dispense cash. And in 2016, a third group used an ATM cash-out scheme to steal over $2 million from banks across India.
Despite these attacks, the overall state of cybersecurity for ATMs in India is fairly good. Most banks have implemented strong security measures, such as encrypting ATM transactions and using multi-factor authentication for withdrawals. Additionally, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued a number of guidelines to help banks improve their ATM security.
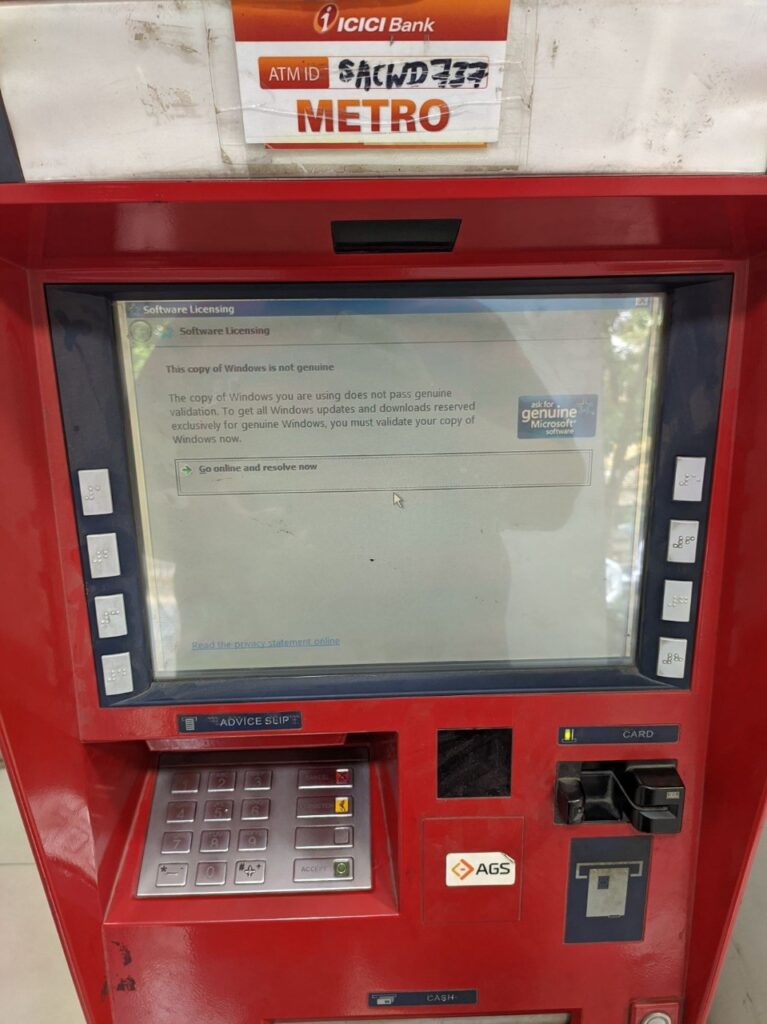
However, there are still some vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. For example, many ATMs in India are still running on outdated operating systems, which makes them more susceptible to attack. Additionally, some ATMs lack basic security features, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
The good news is that steps are being taken to improve ATM security in India. The RBI has mandated that all banks must upgrade their ATMs to run
What is the ATM Industry Doing to Address These Issues?
The ATM industry in India is facing a number of challenges when it comes to cybersecurity. However, there are a number of initiatives being undertaken to address these issues.
One of the most important initiatives is the adoption of the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). This standard provides a set of guidelines for businesses to follow in order to ensure the security of cardholder data.
Another initiative is the setting up of the National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC). This centre will act as a central point for coordination and response in case of any cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure in India.
In addition, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also issued guidelines on cybersecurity for ATMs. These guidelines cover various aspects such as physical security, network security, and software security.
The ATM industry in India is taking these initiatives seriously and is working towards providing a safe and secure environment for users.
The challenges in implementing better security measures
The Current State of Cybersecurity for ATMs in India and What’s Being Done to Prevent It
The ATM industry in India is currently facing many challenges when it comes to cybersecurity. This is due to the fact that there are a large number of ATMs in the country, and many of them are located in remote areas. This makes it difficult to physically secure them, and also makes it challenging to implement security measures such as software updates. In addition, the majority of ATMs in India are owned by small banks or individual operators, which means that there is no central authority that can coordinate security efforts.
Despite these challenges, there are a number of things that are being done to improve the security of ATMs in India. For example, the RBI has issued guidelines on cybersecurity for ATMs, and has mandated that all ATM operators must implement these guidelines by June 2019. In addition, the government has set up a task force to study the current state of ATM security and make recommendations on how to improve it. Finally, some banks are beginning to implement their own security measures, such as installing CCTV cameras at their ATMs.
With these various initiatives underway, it is hoped that the security of ATMs in India will
What can be done to improve security of ATMs in India?
The current state of cybersecurity for ATMs in India is not ideal. In fact, many are vulnerably exposed to cyberattacks that could potentially result in money theft and other serious consequences. To prevent this from happening, there are a number of things that need to be done.
First and foremost, the various ATM manufacturers and providers need to take seriously the issue of cybersecurity and implement proper measures to protect their machines from attack. Unfortunately, this seems to be far from being the case in India. In fact, many of the machines currently in use are highly vulnerable to attack. This is due in part to the fact that they are often outdated and lack the latest security features.
ATM operators also need to take steps to ensure that their machines are properly protected against cyberattacks. They should employ robust security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS). They should also ensure that all users who have access to the machines are properly trained on how to use them safely and securely. Finally, they should keep up with the latest trends in cybersecurity so that their machines are as safe as possible from attack.


